Portal:Nuclear technology
The Nuclear Technology Portal
Introduction

- Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors and gun sights. (Full article...)
- Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2. Generating electricity from fusion power remains the focus of international research. (Full article...)
- A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. (Full article...)
General images -
Selected article -

The incident was reported to the top levels of the United States military and referred to by observers as a Bent Spear incident, which indicates "an unexpected occurrence involving nuclear weapons or nuclear components that does not fall under the NUCFLASH or BROKEN ARROW categories" or "a nuclear incident involving a nuclear weapon/warhead or nuclear component". In the Army and Air Force, this term includes a 'significant incident' as defined in DoD Directive 5100.52".
In response to the incident, the United States Department of Defense (DoD) and USAF conducted an investigation, the results of which were released on 19 October 2007. The investigation concluded that nuclear weapons handling standards and procedures had not been followed by numerous USAF personnel involved in the incident. As a result, four USAF commanders were relieved of their commands, numerous other USAF personnel were disciplined or decertified to perform certain types of sensitive duties, and further cruise missile transport missions from—and nuclear weapons operations at—Minot Air Force Base were suspended. In addition, the USAF issued new nuclear weapons handling instructions and procedures.
Separate investigations by the Defense Science Board and a USAF "blue ribbon" panel reported that concerns existed on the procedures and processes for handling nuclear weapons within the Department of Defense but did not find any failures with the security of United States nuclear weapons. Based on this and other incidents, on 5 June 2008, Secretary of the Air Force Michael Wynne and Chief of Staff of the Air Force General T. Michael Moseley were asked for their resignations, which they gave. In October 2008, in response to recommendations by a review committee, the USAF announced the creation of Air Force Global Strike Command to control all USAF nuclear bombers, missiles, and personnel. (Full article...)
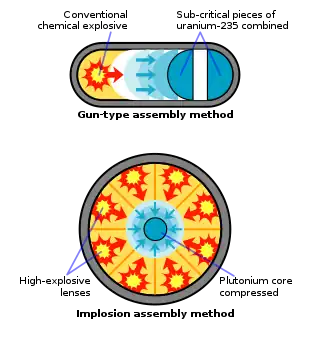
Selected picture -

Did you know?
- ... that part of Keith Foulger's job was to make sure the front and back ends of Britain's first nuclear submarine fitted together?
- ... that campaigning by climate activist Kimiko Hirata halted plans to build 17 new coal-fired power plants following the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan?
- ... that the village of Pstrąże is known as the "Polish Chernobyl" due to its reputation as a ghost town and a former storage site for nuclear weapons?
- ... that after journalist Adele Ferguson's criticism of the U.S. Navy's sex discrimination attracted nationwide attention, she was offered a personal tour of a nuclear submarine?
- ... that the M42 sub-basement was featured in a navy training film as the safest place in New York during a nuclear strike?
- ... that the upcoming SNLE 3G-class nuclear ballistic-missile submarines could remain in service with the French Navy until 2090?
Related WikiProjects
- WikiProject Energy
- WikiProject Technology
- WikiProject Military history
Things you can do
| Parts of this portal (those related to section) need to be updated. Please help update this portal to reflect recent events or newly available information. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (September 2021) |
|
|
Here are some Open Tasks :
|
Selected biography -
Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. (August 27, 1915 – November 4, 2011) was an American physicist who was awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics, for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which had important applications in the construction of atomic clocks. A physics professor at Harvard University for most of his career, Ramsey also held several posts with such government and international agencies as NATO and the United States Atomic Energy Commission. Among his other accomplishments are helping to found the United States Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory and Fermilab. (Full article...)
Nuclear technology news
- 29 March 2023 – Burkina Faso–North Korea relations
- Burkina Faso formally resumes diplomatic relations with North Korea after suspending them in 2017 over the country's nuclear weapons program. (Andolu Agency)
- 25 March 2023 – Pokhran missile incident
- Three surface-to-air missiles are misfired by the Indian Army during an exercise in the Pokhran ranges in the western Jaisalmer district of Rajasthan, India. There are no reports of damage or casualties. (Dawn)
- 25 March 2023 – Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Belarus–Russia relations
- Russian President Vladimir Putin announces that Russia will station tactical nuclear weapons in Belarus by July. The nuclear missiles will be operated by Russian forces. It will be the first time that Russian nuclear weapons have been deployed abroad since 1996. (BBC News) (Reuters)
- 20 March 2023 – North Korea and weapons of mass destruction
- North Korea conducts drills simulating a nuclear counterattack in response to joint amphibious landing exercises by the United States and South Korea. (Reuters)
Related portals
Related topics
Subcategories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
































_conducts_a_fueling_at_sea_(FAS)_with_the_Nimitz-class_aircraft_carrier_USS_George_Washington_(CVN_73).jpg.webp)








-LLNL.jpg.webp)
.svg.png.webp)

.jpg.webp)














.jpg.webp)












