Portal:Tropical cyclones
The Tropical Cyclones Portal
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fuelled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Selected named cyclone -

Typhoon Pongsona was the last typhoon of the 2002 Pacific typhoon season, and was the second costliest United States disaster in 2002, only behind Hurricane Lili. The name "Pongsona" was contributed by North Korea for the Pacific tropical cyclone list and is the Korean name for the garden balsam. Pongsona developed out of an area of disturbed weather on December 2, and steadily intensified to reach typhoon status on December 5. On December 8 it passed through Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands while near its peak winds of 175 km/h (109 mph) 10-min). It ultimately turned to the northeast, weakened, and became extratropical on December 11.
Typhoon Pongsona produced strong wind gusts peaking at 290 km/h (180 mph) 1-min), which left the entire island of Guam without power and destroyed about 1,300 houses. With strong building standards and experience from repeated typhoon strikes, there were no fatalities directly related to Pongsona, although there was one indirect death from flying glass. Damage on the island totaled over $730 million (2002 USD, $1.1 billion 2023 USD), making Pongsona among the five costliest typhoons on the island. The typhoon also caused extreme damage on Rota and elsewhere in the Northern Mariana Islands, and as a result of its impact the name was retired. (Full article...)Selected article -

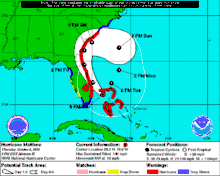
In Maryland and Washington, D.C., the effects of Hurricane Isabel were among the most damaging from a tropical cyclone in the respective metropolitan area. Hurricane Isabel formed from a tropical wave on September 6, 2003, in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. It moved northwestward, and within an environment of light wind shear and warm waters, it steadily strengthened to reach peak winds of 165 miles per hour (266 km/h) on September 11. After fluctuating in intensity for four days, Isabel gradually weakened and made landfall on the Outer Banks of North Carolina with winds of 105 miles per hour (169 km/h) on September 18. It quickly weakened over land and became extratropical over western Pennsylvania the next day.
On September 19, Tropical Storm Isabel passed through extreme western Maryland, though its large circulation produced tropical storm force winds throughout the state. About 1.24 million people lost power throughout the state. The worst of its effects came from its storm surge, which inundated areas along the coast and resulted in severe beach erosion. On the Eastern Shore, hundreds of buildings were damaged or destroyed, primarily in Queen Anne's County from tidal flooding. Thousands of houses were affected in Central Maryland, with severe storm surge flooding reported in Baltimore and Annapolis. Washington, D.C., sustained moderate damage, primarily from the winds. Throughout Maryland and Washington, damage totaled about $820 million (equivalent to $1.21 billion in 2021), with only one fatality due to flooding. (Full article...)Selected image -
Selected season -

The 2020 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was the costliest North Indian Ocean cyclone season on record, mostly due to the devastating Cyclone Amphan. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and November, with peaks in late April to May and October to November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. The season began on May 16 with the designation of Depression BOB 01 in the Bay of Bengal, which later became Amphan. Cyclone Amphan was the strongest storm in the Bay of Bengal in 21 years and would break Nargis of 2008's record as the costliest storm in the North Indian Ocean. The season concluded with the dissipation of Cyclone Burevi on December 5. Overall, the season was slightly above average, seeing the development of five cyclonic storms.
The scope of the season is limited to the Indian Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere, east of the Horn of Africa and west of the Malay Peninsula. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean – the Arabian Sea to the west of the Indian subcontinent, abbreviated ARB by the India Meteorological Department (IMD); and the Bay of Bengal to the east, abbreviated BOB by the IMD. (Full article...)Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones

Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2023)
- No active systems
- East and Central Pacific (2023)
- No active systems
- West Pacific (2023)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2023)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2022–23)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2022–23)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2022–23)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2022–23)
- No active systems
Last updated: 10:22, 8 April 2023 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

April 7
- 1982 - Cyclone Dominic made landfall on the northwestern coast of Queensland, Australia. Dominic caused at least $3.6 million of damage, mostly in the Darwin area.
- 1999 - Cyclone Gwenda (pictured), as a Category 2 cyclone, makes landfall over Port Hedland, Western Australia after it reached peak of 10-minute sustained winds of 220 km/h (140 mph).

April 8
- 1979 - Cyclone Idylle remains active in the eastern side of the South-West Indian Ocean basin, just before reaching peak strength and entering the Australian region basin.
- 1984 - Cyclone Kamisy (pictured) reaches peak intensity as an Intense tropical cyclone, just before brushing the northern part of Madagascar and was dubbed as the worst storm to hit the country since 1911. Kamisy killed 69 people and caused 810 billion Ariary in damages (about US$250 million).

April 9,
- 1998 - Tropical Storm Gemma attains peak strength over the South-West Indian Ocean, with winds of 85 km/h (50 mph), according to the MFR. The JTWC, however, classified Gemma's peak as a Category 1 tropical cyclone two days later.
- 2005 - Cyclone Juliet (pictured) reaches peak strength, with 10-minute sustained winds of 205 km/h (125 mph) and a minimum central pressure of 905 hPa (mbar).
Did you know…




- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
- …that Hurricane Agatha (pictured) was the strongest Pacific hurricane to make landfall in Mexico in May since records began in 1949?
- …that Cyclone Raquel (track pictured) travelled between the Australian and South Pacific basins between the 2014–15 and 2015–16 seasons, spanning both seasons in both basins?
- …that Cyclone Amphan (pictured) in 2020 was the first storm to be classified as a Super Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal since 1999?
General images -
 Featured list -
Featured list -

The 2003 Atlantic hurricane season was an active Atlantic hurricane season with tropical activity before and after the official bounds of the season – the first such occurrence in 33 years. The season officially began on June 1, 2003 and ended on November 30. However, a pre-season storm, Tropical Storm Ana, led to the season starting on April 20, and storm activity continued through December 11. The timeline includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned upon, has been included. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipations during the season.
This season had 21 tropical depressions, of which, 16 became named storms. Of these, 7 strengthened into hurricanes with 3 intensifying into major hurricanes. Hurricane Fabian, Hurricane Isabel, and Hurricane Juan had their names retired due to the impact caused in Bermuda, the eastern United States, and Nova Scotia respectively. Both Fabian and Juan were the worst hurricanes to hit their respective areas, causing $450 million in damages and 16 fatalities. Hurricane Isabel was the strongest, deadliest, and costliest storm of the season. Isabel peaked as a Category 5 hurricane over the open waters of the Atlantic; however, it weakened to a Category 2 before impacting the east coast of the United States, causing $3.6 billion in damages and 51 fatalities. (Full article...)Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Meteorology is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general.
WikiProject Weather – Non-tropical storms task force – coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on notable extratropical cyclones, and the two projects share numerous overlaps.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals













.jpg.webp)






.jpg.webp)

_(50).jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)




